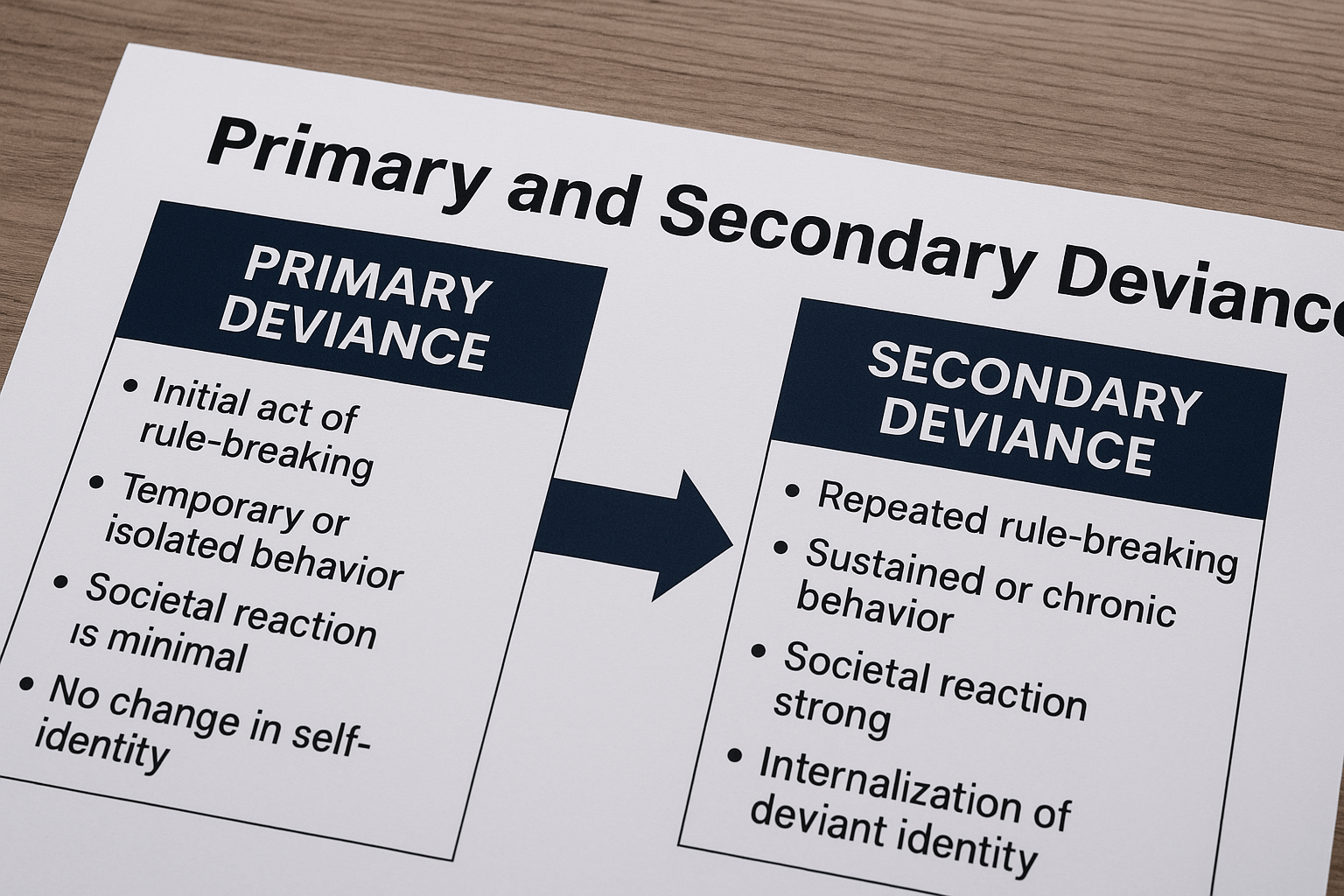
The Concept of the Serial Killer: A Scientific Perspective
Introduction The concept of the serial killer has long fascinated criminologists, psychologists, sociologists, and even the general public. Unlike other forms of homicide, serial killing involves a repetitive cycle of violence, psychological compulsion, and symbolic meaning. The serial killer is not only a legal category but also a social and cultural construct, deeply embedded in … Read more