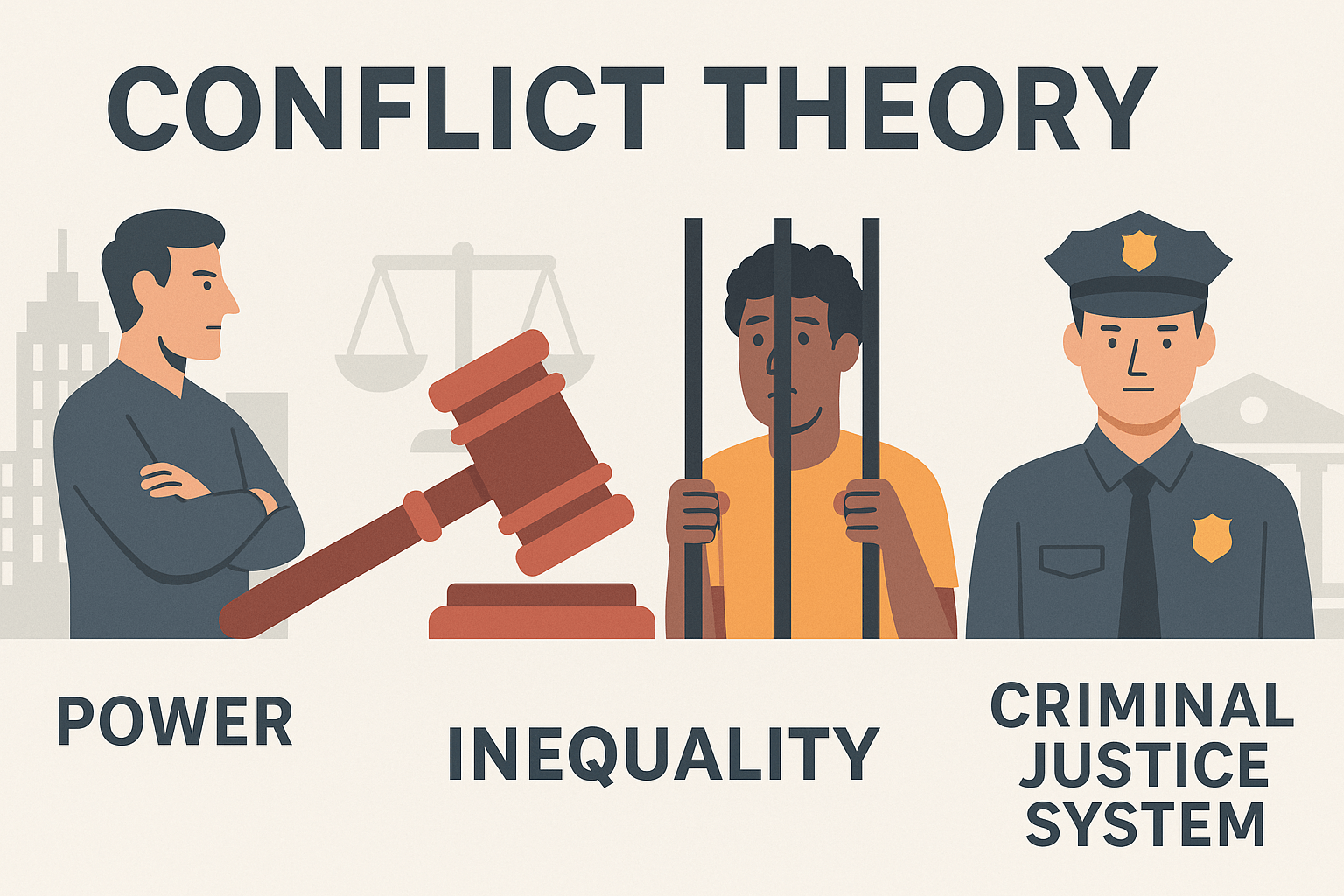
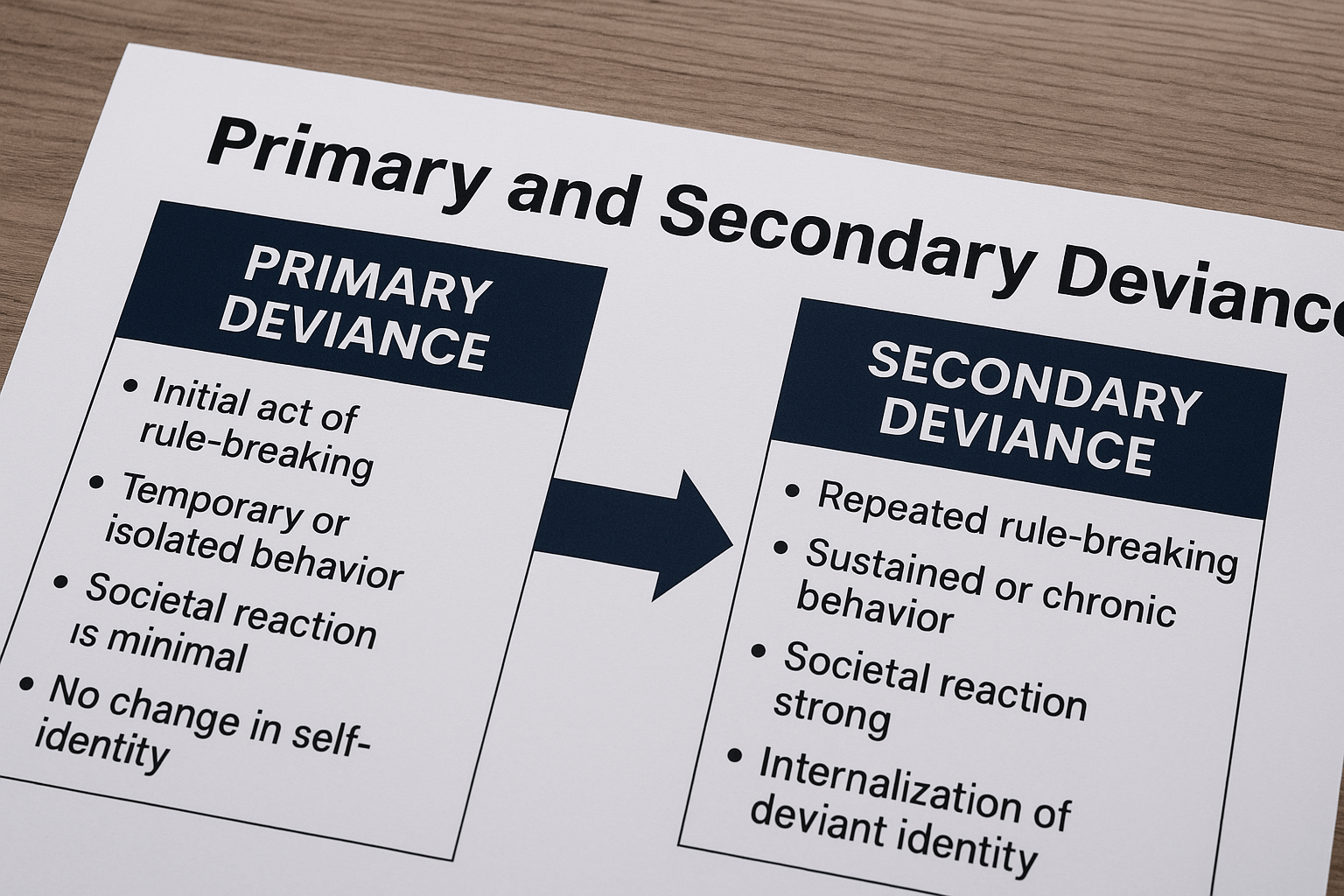
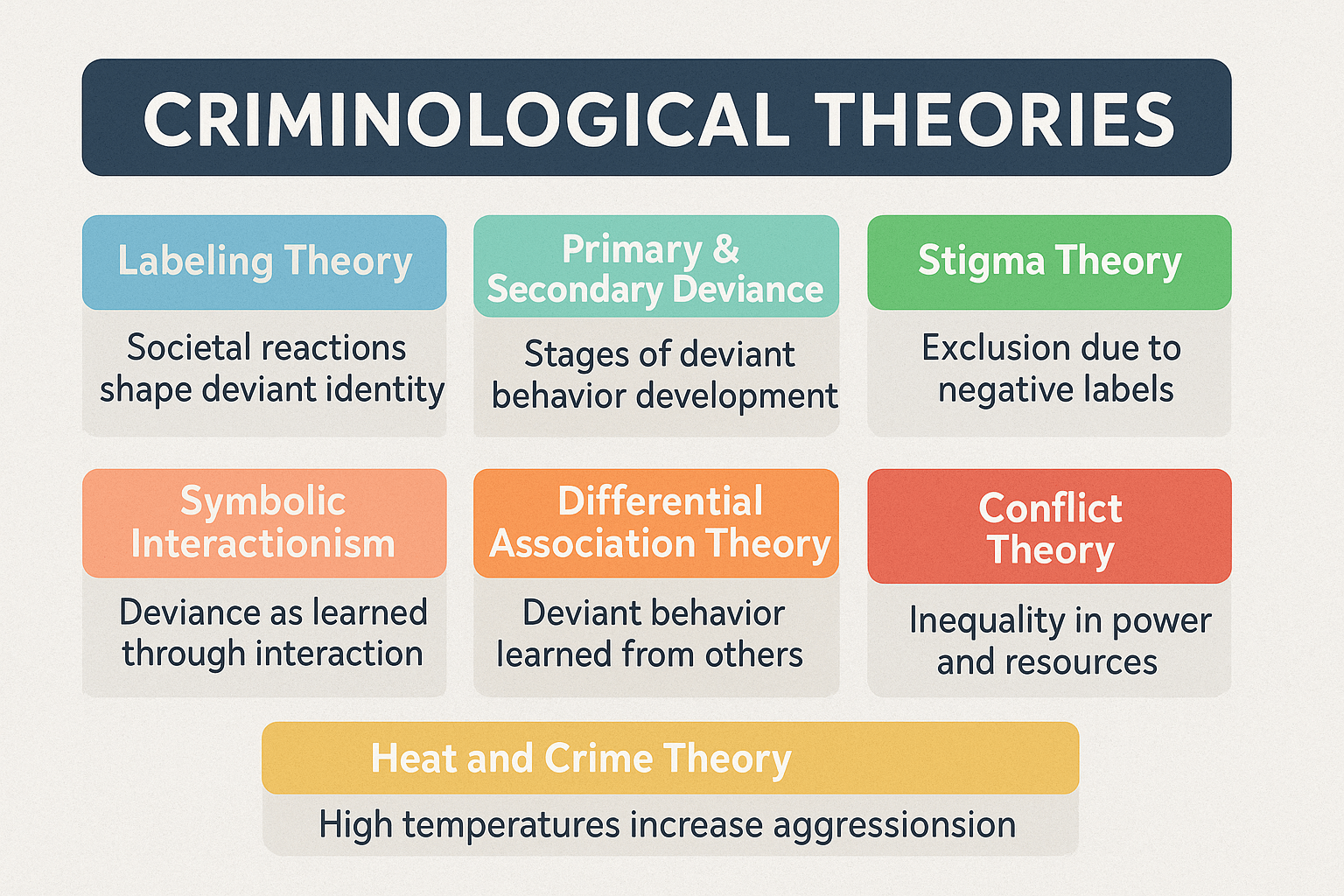
Schizophrenia and Psychopathy in Criminology: A Comparative Analysis
Introduction: Schizophrenia and Psychopathy The study of criminal behavior has always been closely linked with the understanding of human psychology and mental health. From the earliest days of criminology, scholars have attempted to explain why certain individuals engage in deviant or violent acts while others, despite facing similar conditions, do not. Within this context, the … Read more